Viscosity
Imagine spilling a cup of honey and a cup of water on the floor. Honey takes more time to spill and spread out, but water spills and spreads faster. This is because honey's viscosity is more than water's.
Viscosity is the property of a fluid (liquid or gas) to oppose its flow.
There are a lot of molecules in the fluid. These molecules interact with one another. If the molecular interaction inside the fluid results in low internal friction, the viscosity is low and the fluid can flow easily (like water). If the interactions lead to high internal friction, the viscosity is large, and the fluid cannot flow easily (like honey).
Consider a small amount of oil in a tumbler. Shaking the tumbler leads to disturbance and causes the oil to move.
Consider a layer of a liquid as shown in figure 1. Let us assume a force 'F' is acting on the surface. The upper layer is moving with a velocity 'v'. And the lower layer is at rest (v=0). Figure 2 represents the same layer of the liquid in 3D which has height 'd' and surface area 'A'.
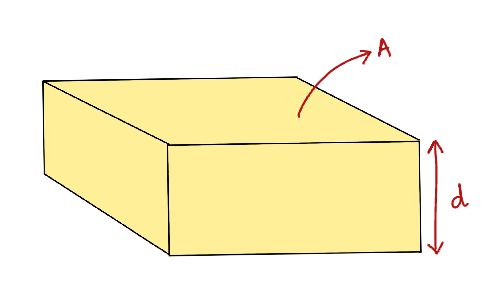
Figure 2
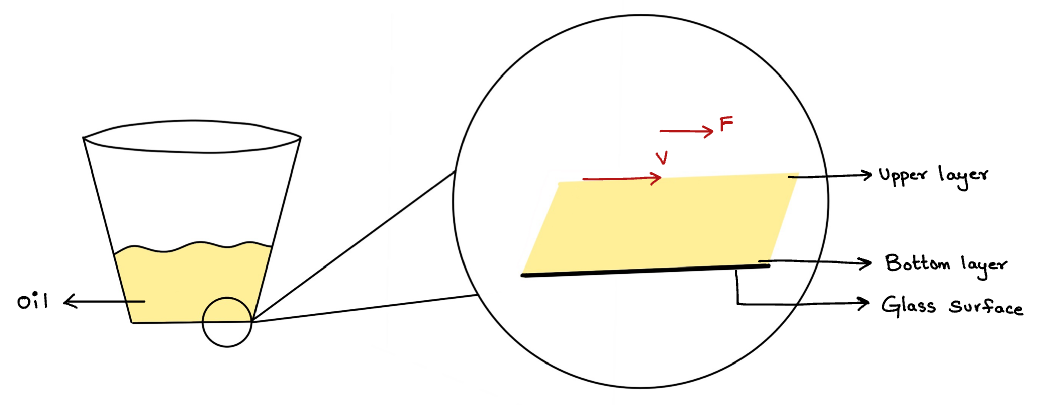
Figure 1
The force is directly proportional to the velocity, surface area, and inversely proportional to the distance (height). The proportionality constant in this case is the viscosity of the fluid (represented by Greek letter η).
The formula can be written as -
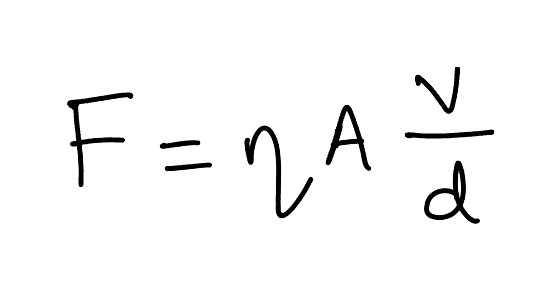
There are various units to viscosity. The SI unit of viscosity can be deduced using the above equation as shown.
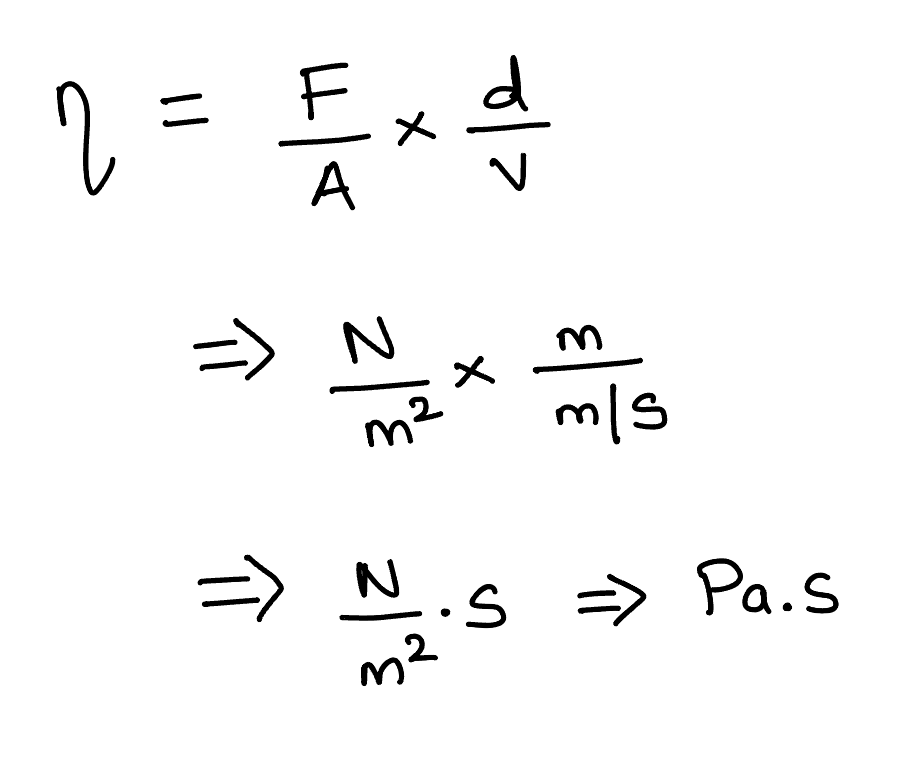
There are various units to viscosity. The SI unit of viscosity can be deduced using the above equation as shown.
The SI unit of Viscosity is Pa.s (Pascal second). Other most commonly used units of viscosity include P and centipoise (cP).
Conversions - 1 Pa.s = 10 P = 1000 cP
Viscosity of the fluids vary when there is a rise or fall in the temperature. With an increase in temperature, the viscosity of gases and liquids behaves differently.
In liquids, increasing the temperature causes a decrease in the viscosity. This is because the increased temperature gives thermal energy to the liquid molecules and thus causing them to move easily.
In gases, an increased temperature gives thermal energy to the gases and causes the molecules to move more freely. This random behavior causes a lot of collisions among the gas molecules and increase in the viscosity.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to its flow
Viscosity is due to the inter-molecular interactions in the fluid
Viscosity is measured in units like - Pascal second, poise, and centipoise
Viscosity of liquids decreases when temperature is increased
Viscosity of gases increases when temperature is increased
Sources
- https://www.princeton.edu/~gasdyn/Research/T-C_Research_Folder/Viscosity_def.html#:~:text=Viscosity%20is%20a%20measure%20of%20a%20fluid's%20resistance%20to%20flow.&text= A%20fluid with%20large%20viscosity%20resists,when%20it%20is%20in%20motion.
- https://physics.info/viscosity/
- https://www.rheosense.com/what-is-viscosity
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viscosity