What is DNA?
This article covers the following information: the definition of DNA, why DNA is necessary, what DNA is made up of, and how it is packed and stored inside cells.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in all living organisms. It carries all the information about the organism and aids in its growth, development, and proper functioning.
Why is DNA important ?
DNA is the hereditary material transferred from the parental generation to the offspring. DNA performs many activities, including protein synthesis. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism, and they carry out various functions to keep the organism alive. Therefore, DNA is of great importance.
What is DNA made of?
DNA has three basic units. They are:
Deoxyribose sugar (add structures)
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous bases
1. Deoxy ribose sugar:
It is a 5-carbon sugar that forms the backbone of the DNA. The carbon atoms are named from 1' to 5'
(Figure 1).
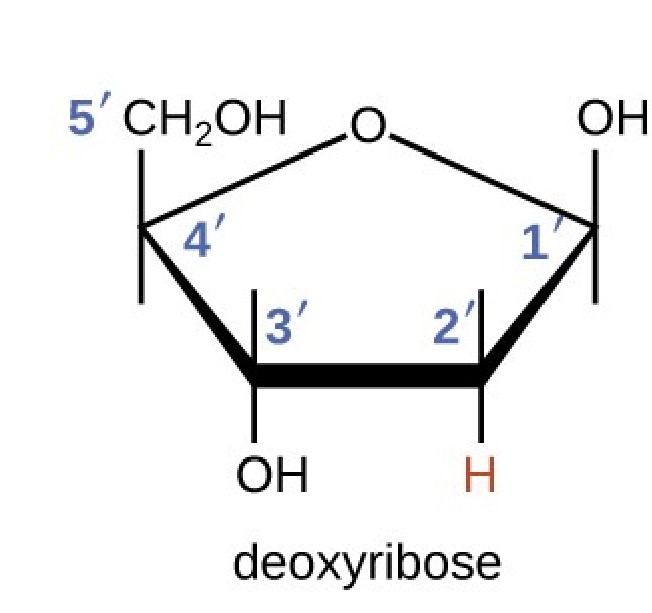
Figure 1
2. Phosphate group:
Forms linkage between the sugar molecules to create a long chain of DNA strands. (Figure 2). DNA has a total negative charge because of the phosphate groups.
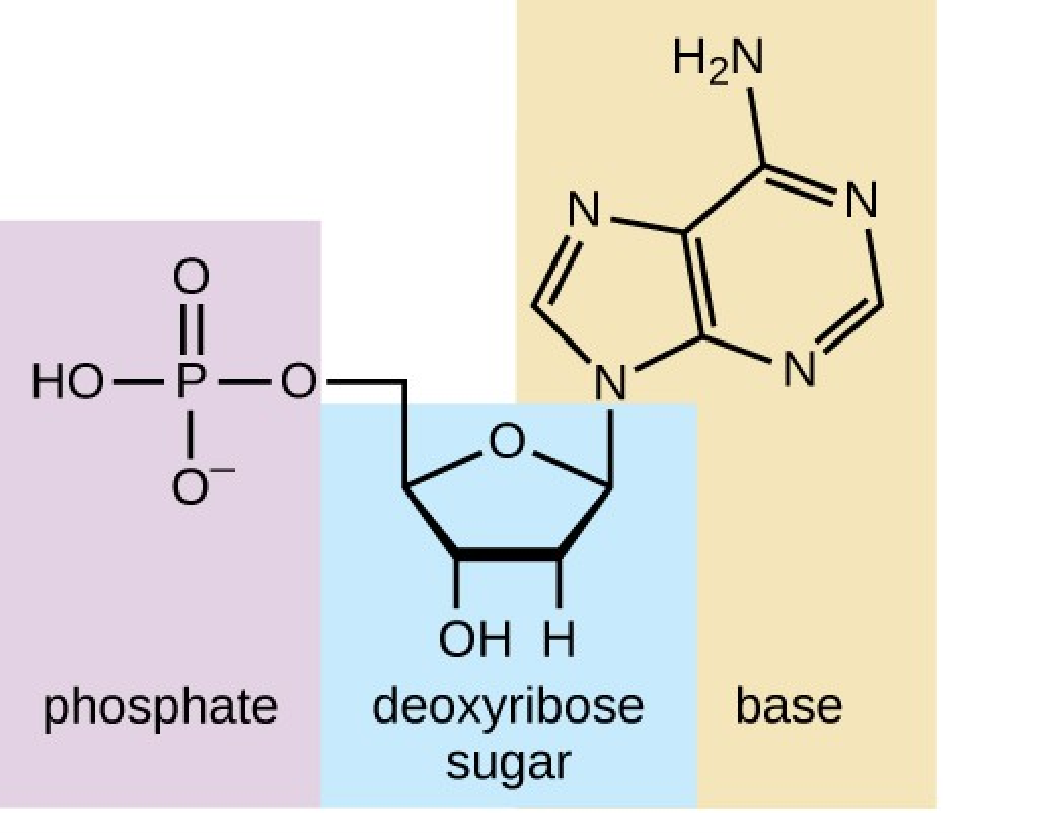
Figure 2
3. Nitrogenous bases:
They carry the genetic code.
They are of two types (Figure 3):
Purines
Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T)
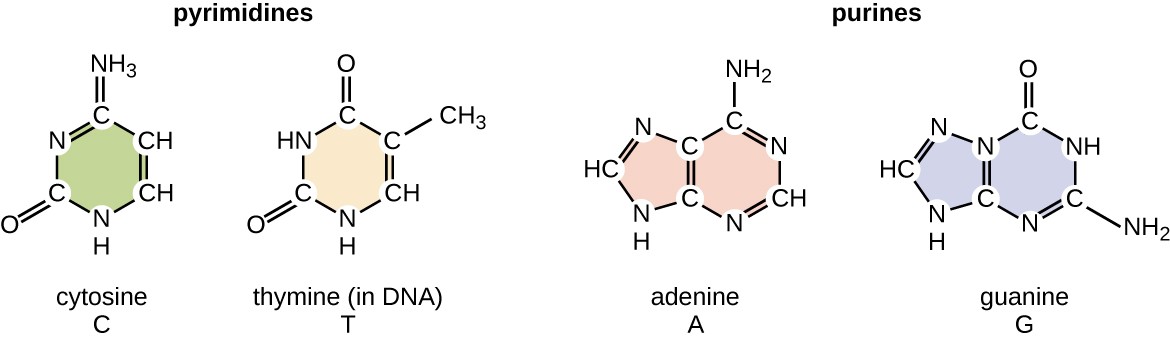
Figure 3
Adenine binds to Thymine (A-T), and Guanine binds to Cytosine (G-C) (Figure 4).
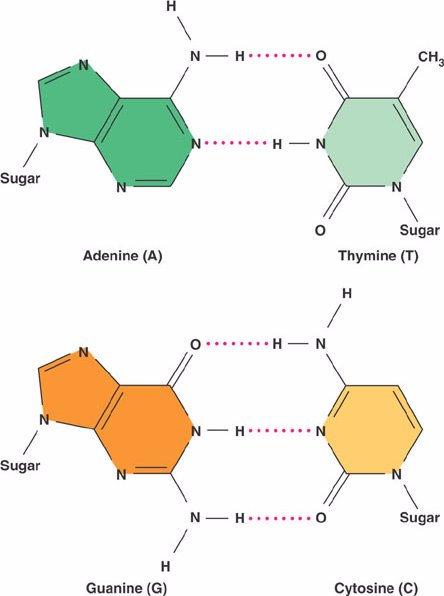
Figure 4
How are the molecules bound to each other?
Sugar molecules and Phosphate group - Phosphodiester bond
Sugar molecules and Nitrogenous base - Glycosidic bond
Nitrogenous base and Nitrogenous base - Hydrogen bond (2 hydrogen bonds between Adenine and Thymine, 3 hydrogen bonds between Guanine and Cytosine) (Figure 5 & 6)
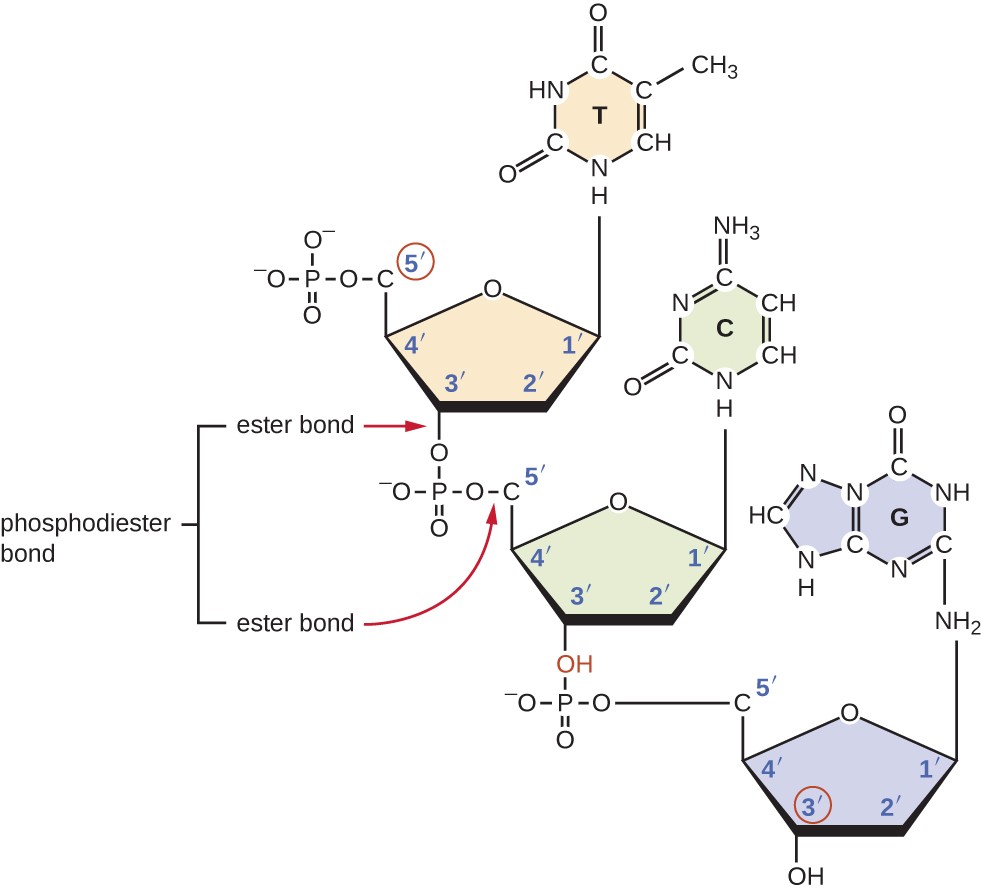
Figure 5
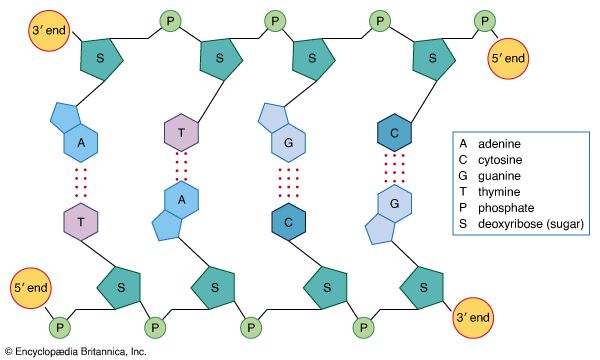
Figure 6
Chargaff's rule states that - A+G=T+C
Amount of Adenine = Amount of Thymine
Amount of Guanine = Amount of Cytosine
Nucleoside - Sugar + base
Nucleotide - Base + phosphate group + sugar
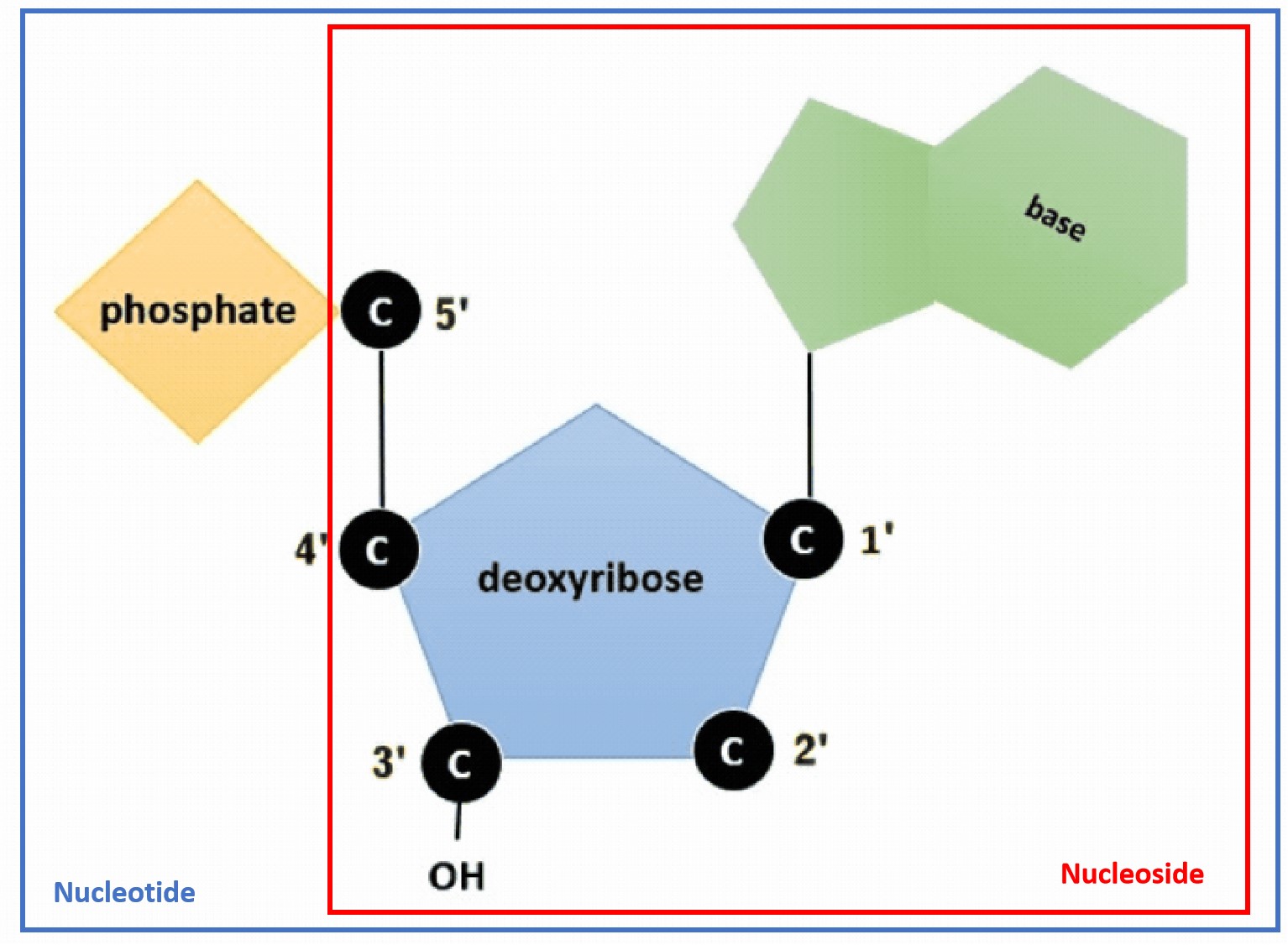
Figure 7
Overview of the DNA structure
In Figure 8 you can see how the nitrogenous bases Adenine and Thymine (A-T, 2 hydrogen bonds) and the nitrogenous bases Guanine and Cytosine (G-C, 3 hydrogen bonds) make a base pair.
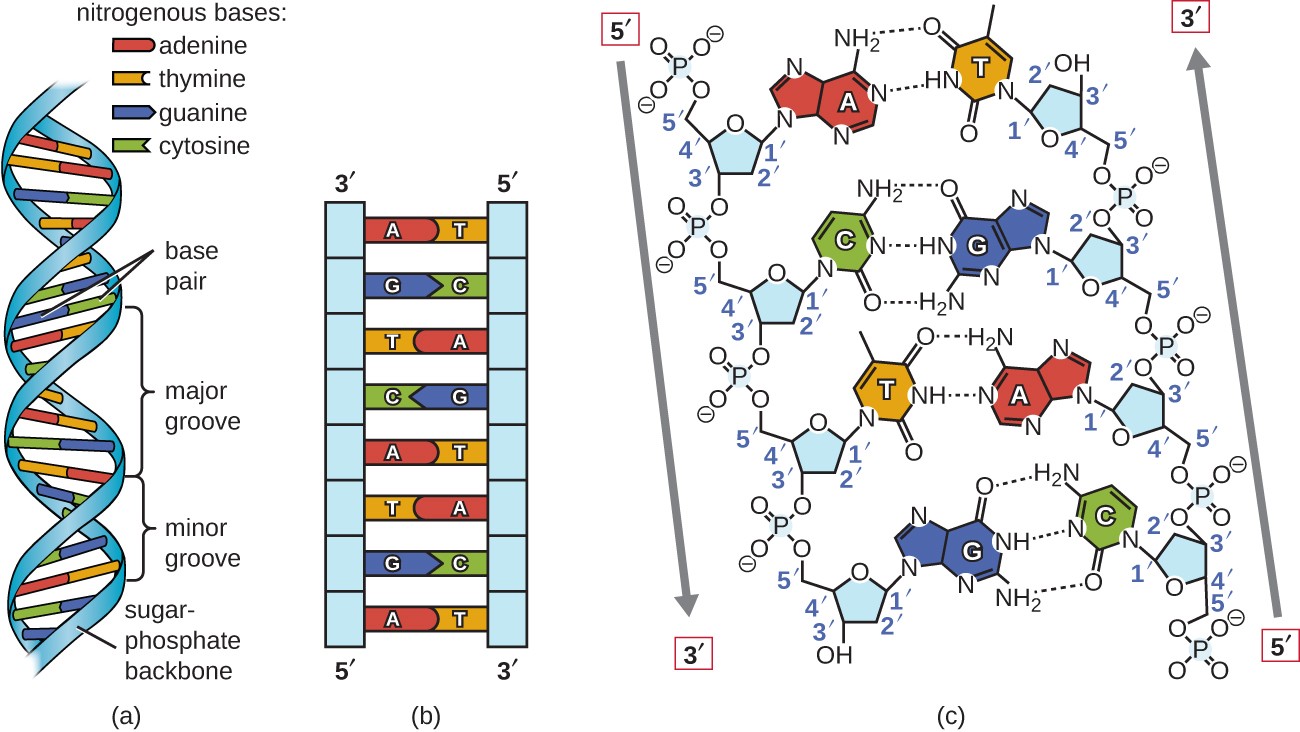
Figure 8 - Overview of the DNA structure
How long is DNA and how is it packed to fit into the tiny cells?
DNA carries a vast amount of information about all the proteins required for the human body. Consequently, DNA is a very long strand. For instance, human DNA, when combined with all the DNA lengths in every cell of the human body, adds up to 100 trillion meters. However, the body can store all this DNA in tiny cells, thanks to histone proteins.
Histones are proteins that allow DNA to be stored compactly. Histone proteins have a positive charge, while DNA is negatively charged. They bind very tightly to each other, with the DNA strand wrapping around the histone. DNA that has wrapped around a histone protein is called a nucleosome. These nucleosome units further coil and form tubular structures. These structures undergo supercoiling to give rise to chromosomes that store genetic information.(Figures 9 and 10)
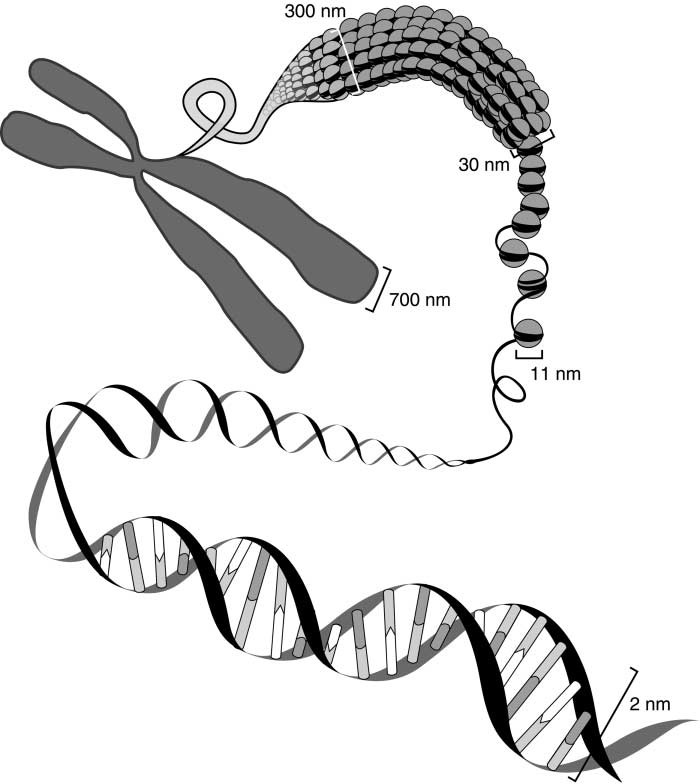
Figure 9
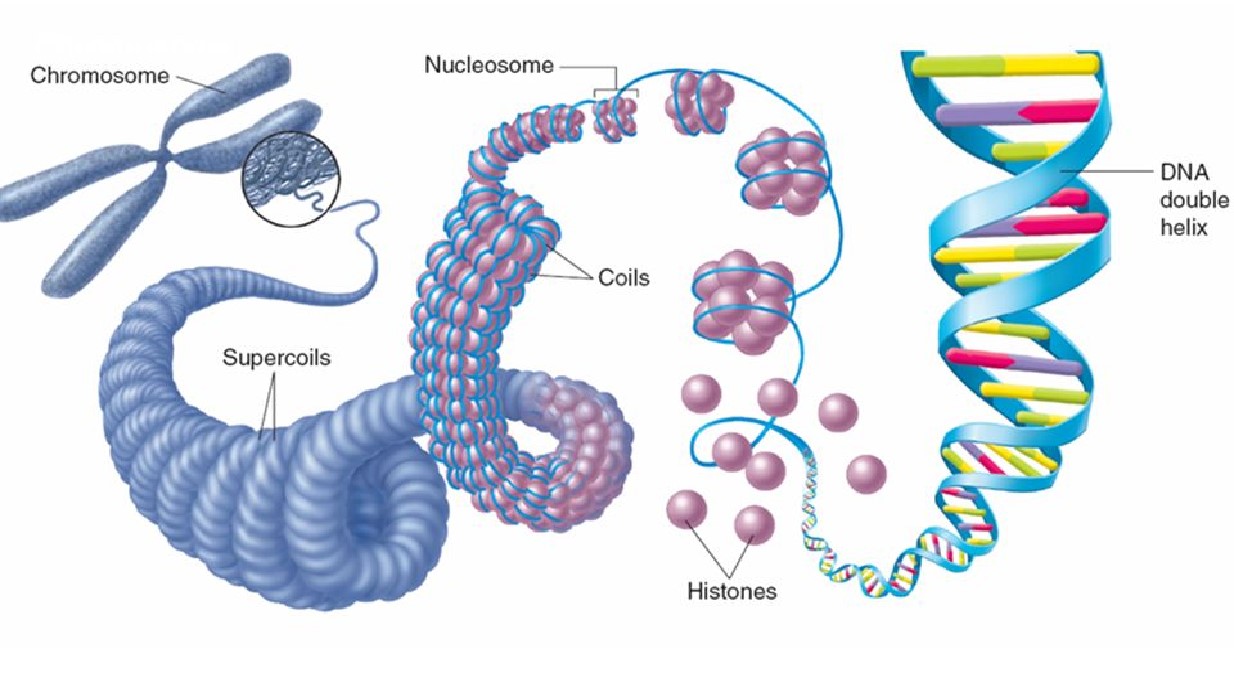
Figure 10
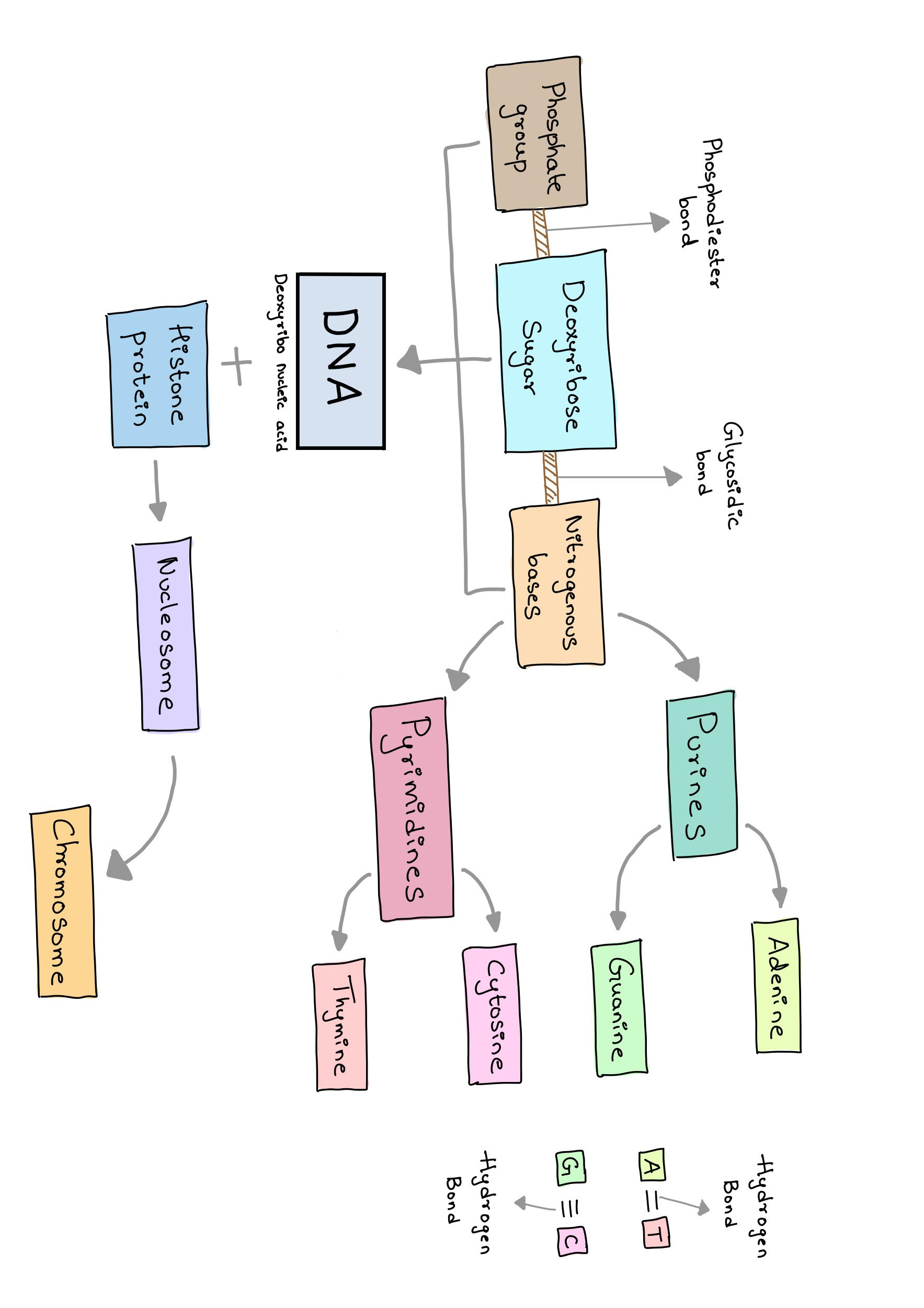
Figure 11 - Mind map
Sources
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/understanding/basics/dna/#:~:text=DNA%2C or deoxyribonucleic acid%2C is,body has the same DNA.
- https://www.britannica.com/science/DNA
- https://www.yourgenome.org/facts/what-is-dna/
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/University_of_Arkansas_Little_Rock/Genetics_BIOL3300_(Fall_2022)/Genetics_Textbook/01%3A_Chemistry_to_Chromosomes/1.01%3A__The_Structure_of_DNA
- https://biologydictionary.net/deoxyribose/
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/phosphate-group.html#:~:text=The phosphate group present in,the single strand of DNA.
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/dna-packaging-nucleosomes-and-chromatin-310/
- https://kids.britannica.com/kids/assembly/view/2659
- https://socratic.org/questions/what-are-the-nitrogen-bases-in-a-dna-molecule
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-mcc-microbiology/chapter/structure-and-function-of-dna/
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/University_of_Arkansas_Little_Rock/Genetics_BIOL3300_(Fall_2022)/Genetics_Textbook/01%3A_Chemistry_to_Chromosomes/1.01%3A__The_Structure_of_DNA