Introduction: Systems of Linear Equations - Part 1
1 Overview
Content
In this course you will learn at which point two straight lines intersect. The concepts of the intersection point as well as the linear system of equations (with two unknown variables) are introduced. At the end you will be able to solve such a system using elimination by equating coefficents.
Prerequisites
You should know what a linear equation is and how to transform it. Furthermore, it is important that you can read points from a coordinate system and use them again. Since you will be dealing with straight lines and their equations in this course, you should know how to set up such a straight line equation and draw it.
Duration
This course takes about 1.5 hours.
2 An unequal race (1/2)
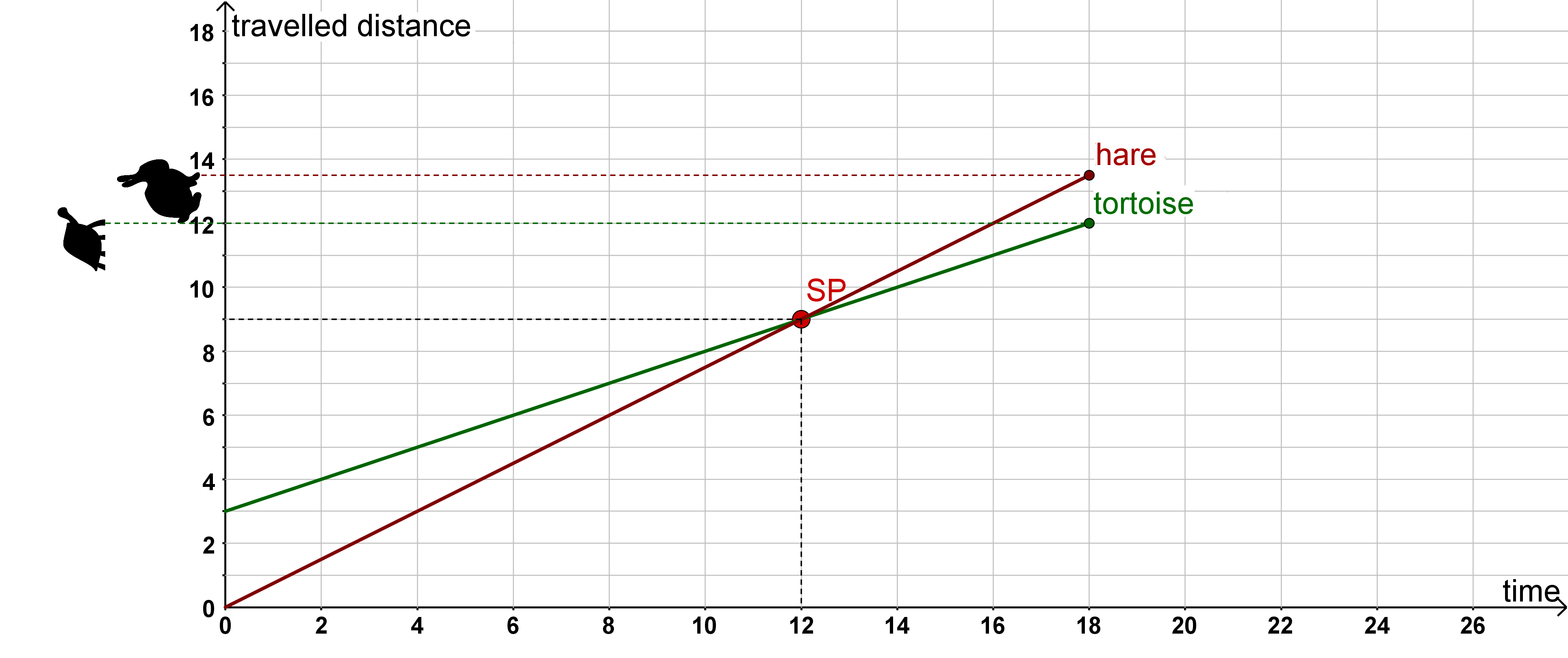
The hare and his best female friend the tortoise start a race. Of course, the hare wants the whole thing to be fair. Therefore he gives the tortoise, who is a bit slower, a little head start. She may start meters further in front.

The hare is now very excited. After all, he doesn't know if the lead was too much and he won't catch up with the tortoise in the race. But he hopes to have a chance and win the race.

3 An unequal race (2/2)
Click on "Start race!" to view the race.
On the x-axis you see the elapsed time since the start,
on the y-axis the distance already covered. On the left side you can also see the current position of the hare and the tortoise.
4 What is an intersection point? (1/2)
As you could observe from the animation, the hare was able to overtake the tortoise. So on their race track there must be a meeting point of the two. This point is thus the answer to the question:
"When and where do the animals meet?"
You will find the answer to this question in several ways in this course.
Quick exercise:
Write down the two linear function equations for the graphs of the tortoise and hare.
5 What is an intersection point? (2/2)
Since points in the coordinate system are always expressed by and , the axis "time" is set as -axis and "distance travelled" as -axis.
The straight line equations from the story now look like this:
Tortoise:
Hare:
So the point where two straight lines cross is the meeting point mentioned above. This is called an intersection point in mathematics. By reading off the intersection point from the graph, you can find the solution to the problem.
Check the intersection point
Once you have read an intersection point from the graph, you can substitute it into your two straight line equations to check it. The coordinates of the intersection are .
Tortoise:
Hare:
Insert the coordinates of the intersection.
Tortoise:
Hare:
If you get two true statements, you have read off the correct intersection.
Tortoise:
Hare:
Since both statements are true, you know that you have determined the intersection correctly.
6 Example: Intersection points
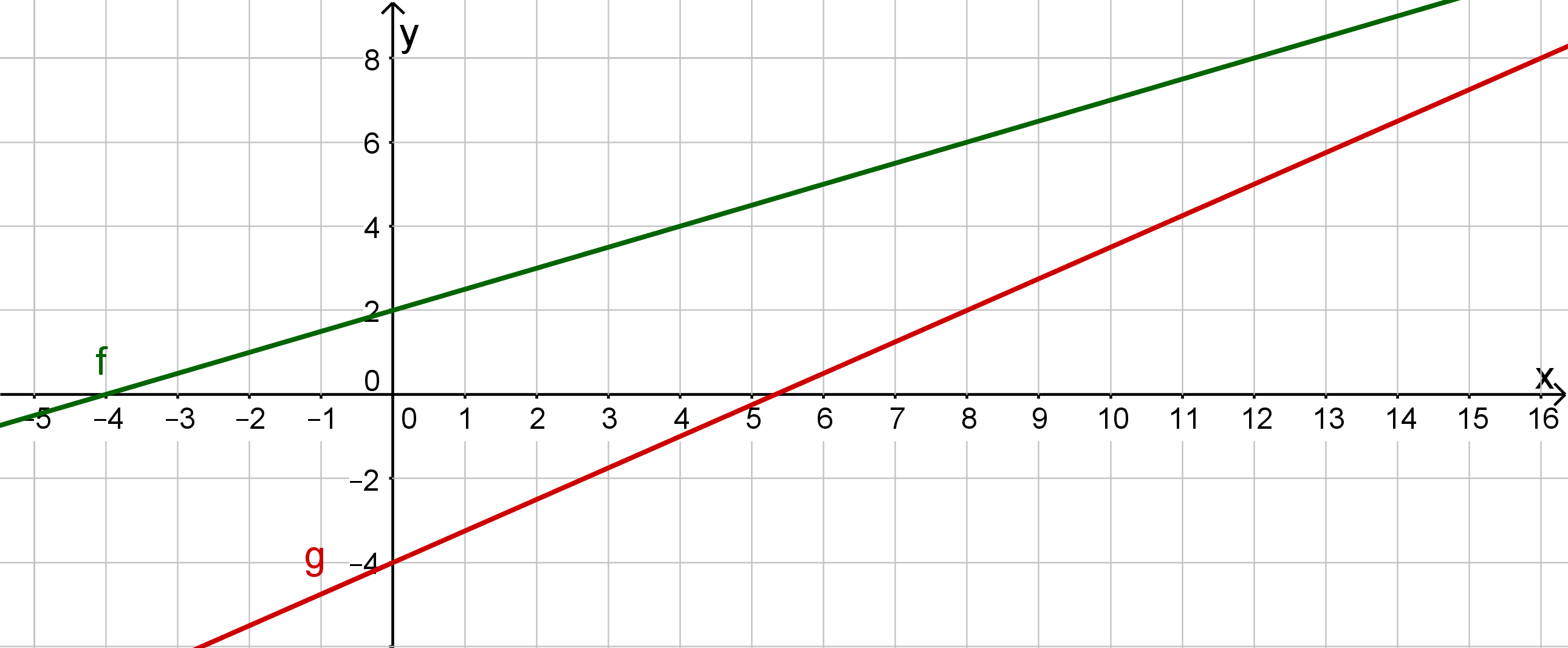
Now the hare and the tortoise race again, but this time the tortoise has a lead of .
The straight line equation for the tortoise and the straight line equation for the hare are now given by:
Tortoise:
Hare:
Again, we want to find out at what time the hare overtakes the tortoise.
a) Draw the equations of the straight lines in the coordinate system.
b) Read off the intersection point from the drawing.
c) Interpret what this intersection point means for the meeting point of both animals.
7 Exercises: Intersection points
Loading
Loading
Under Construction
8 What is a linear system of equations?
If the hare leaves his friend too big a head start at the beginning, the hare may never overtake the tortoise or the meeting point may be so late that your page is not big enough to capture the meeting point.
The graphical solution is therefore not always useful.
How do you proceed in such a case?
In the above example, you worked with two straight lines whose equations you know. One possible way to write a system of equations is to write the equations one below the other and number them with Roman numerals. This looks as follows:
What is a linear system?
A linear equation is an equation depending linearly on one or more unknowns (variables), such as and .
Several linear equations with the same variables, for example and , form a system of linear equations. The goal is to find values for the variables such that all equations are satisfied simultaneously.
9 Why do you need a mathematical procedure?
As mentioned on the last page, you can not always read off the solution, i.e. the intersection point, graphically.
In this case, you can only calculate the solution.
To understand how the different solution methods work, you should first think about what is the determining feature of an intersection.
Think a bit
How do you detect an intersection?
10 Two lines - one common point
Graphical peculiarity
The intersection point lies on both straight lines.
For the -value of the intersection point, both lines provide the same -value.
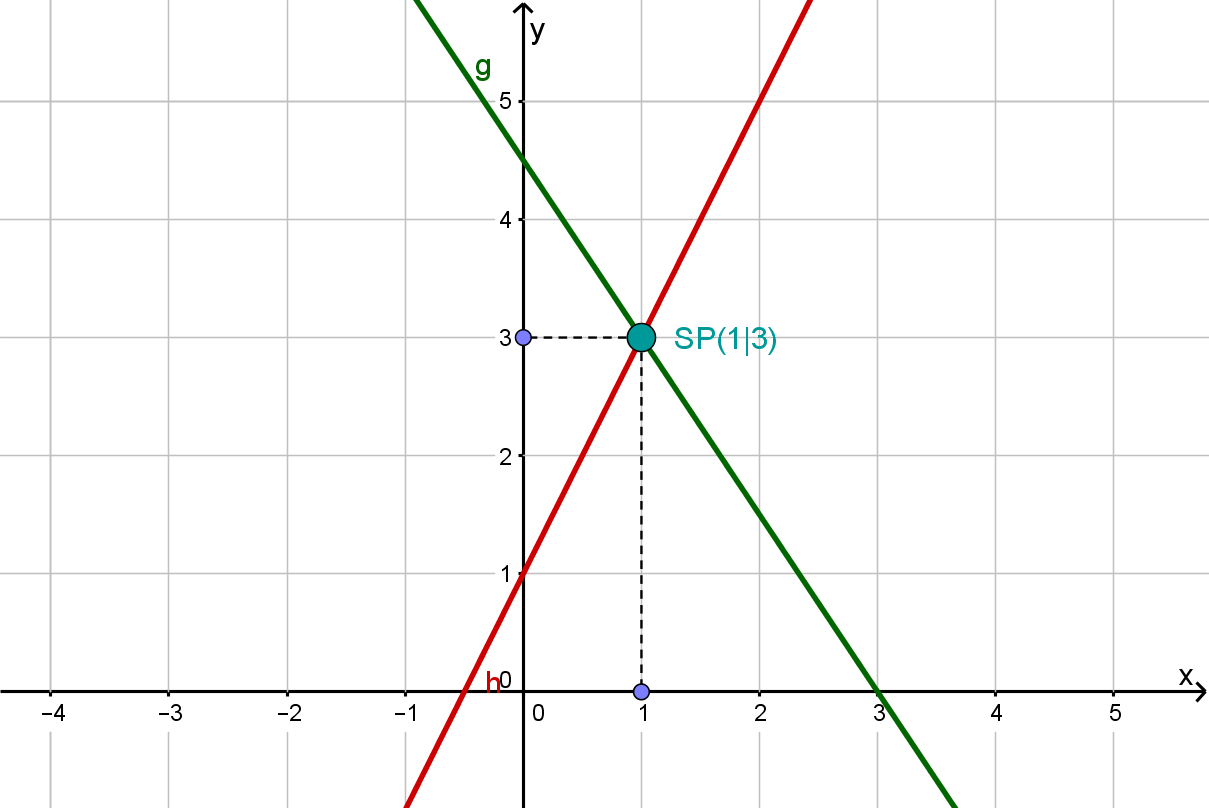
Computational peculiarity
At the intersection point both equations of the equation system are fulfilled!
So if you plug the intersection point into both equations, you get the same, true statement!
Intersection point:
Line g:
Line h:
11 Elimination by equating coefficients (1/2)
The intersection point is a point that lies on both lines. You can use this to calculate the intersection of the two functions.
The method used for this is called elimination by equating coefficients.
How does elimination by equating work?
As an example, consider two straight lines from the previous slides in the course. Write them down as a system of linear equations:
Since you are looking for a point where the two -values are equal, the right part of the equation must also have the same value:
Now you can equate the two right sides:
Exercise
Solve the first equation for !
12 Elimination by equating coefficients (2/2)
Solve the first equation for .
Plug that into one of both equations
To demonstrate that it really doesn't matter which of the two equations you use, here are both equations.
So the intersection point of both lines is !
13 Elimination by equating - step by step
You have just seen how the equation procedure was applied in a specific example. Now we will look again in general how the procedure works.
Basic requirement
The two equations in your system of equations must both be solved for the same term! In this term there should be an unknown (often or ), which is then no longer on the other side.
Example 1
Example 2
Step 1
Put together the two sides of the equations that are not equal.
Example 1
Example 2
Step 2
Solve for the other variable.
Example 1
Example 2
Step 3
Plug the first solution into one of both equations.
Example 1
In :
Example 2
In :
14 Example: Elimination by equation coefficients
Consider the linear system
Calculate the coordinates of the intersection point of the two lines using elimination by equationg coefficients! Berechne die Koordinaten des Schnittpunktes der zwei Geraden, indem du dazu das Gleichsetzungsverfahren benutzt!
Solution
To apply the elimination by equationg coefficients, you must solve the two equations either for or for . Since a line equation has the form , it is easier to solve the equations for .
Keep in mind how to transform equations.
Solve for one variable
15 Example: Elimination by equation coefficients
Apply the elimination
The elimination by equating coefficients ensures that only one of the two variables remains.
To do this, you have just solved both equations for . You can then set equal both equations, since in a linear system of equations the variables and satisfy both equations and .
Now plug into or . To make the calculation easier, we may take the first equation.
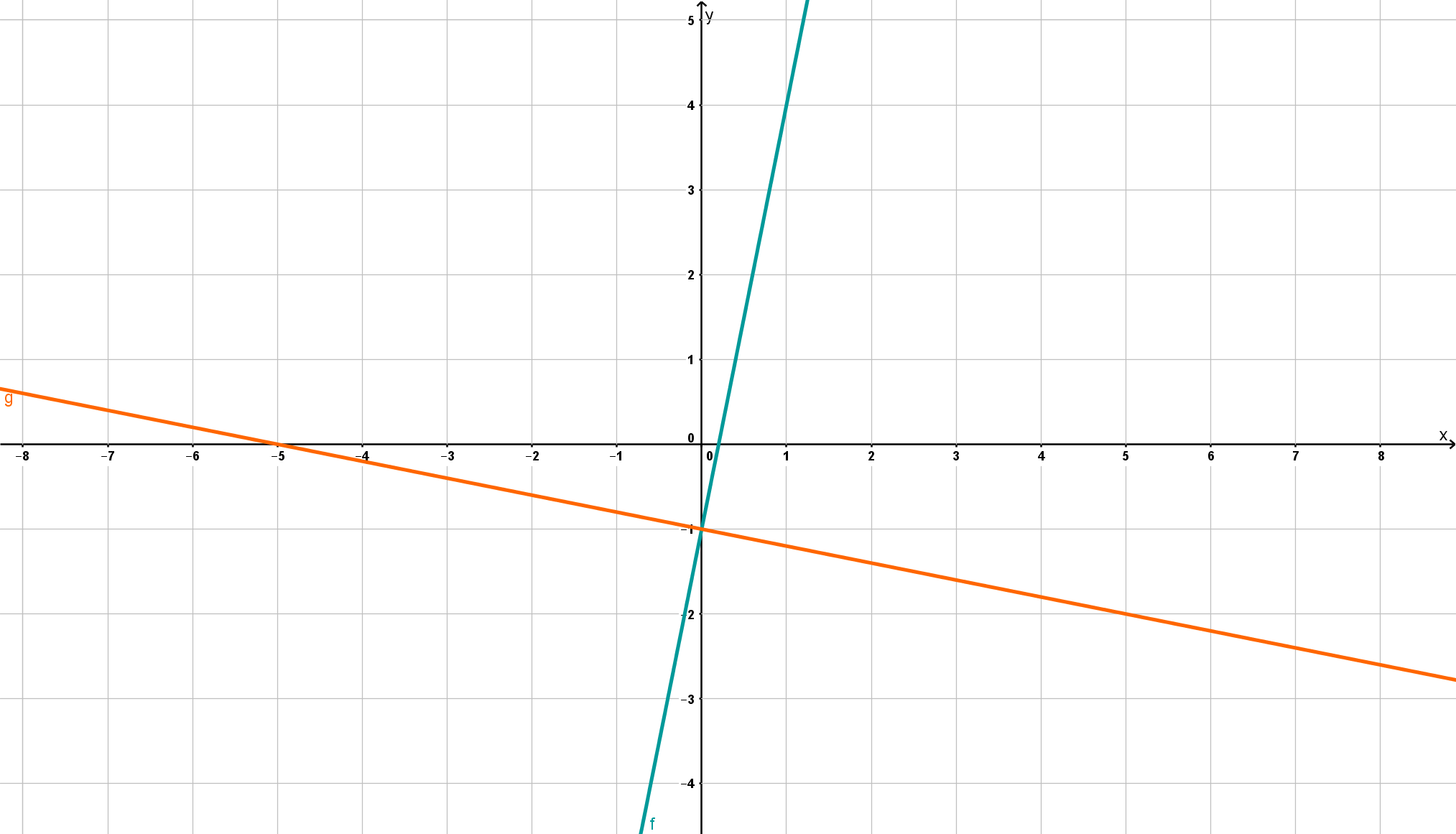
So the intersection point of both lines is .
To check if your calculated intersection is correct, you can draw the straight lines in a diagram. On the left you can see where they intersect.
16 Exercises: Elimination by equation coefficients
Loading
Loading
17 Summary
Intersection point
You learned in this course what an intersection point is and how to read it off.
Two straight lines intersect at an intersection point; both equations of the straight lines are satisfied at the same time.
Linear system of equations
You now know that a linear system of equations consists of two (or more) linear equations. These equations depend on the same variables (usually denoted and ).
Number the equations with Roman numerals so that you don't lose track of them.
You are looking for the solution of the linear system of equations, which is the point at which all equations yield true statements. That means: If you plugthe point into the equations, something like comes out. (Hint: Plug and into the above system).
If you transform all equations of the sysetm into straight line equations of the form , the solution of the equation system is exactly the intersection of these straight lines.
Elimination by equating coefficients
If you cannot read off the intersection or cannot read it off precisely enough, you can calculate it. To do this, you use the elimination by equating coefficients, which gives you the solution of the system in three steps:
Equating: Set equal equations and .
Solving: Solve the resulting equation for one variable.
Plugging in: By substituting into the equation or you get the value of the other variable.
18 Show what you can do!
Loading