Sine and Cosine theorem on a triangle
The sine and cosine theorems establish relationships between side lengths and angles in any triangle.
For any triangle with sides , , and the respective opposite angles , , we have the:
Sine theorem
Cosine theorem
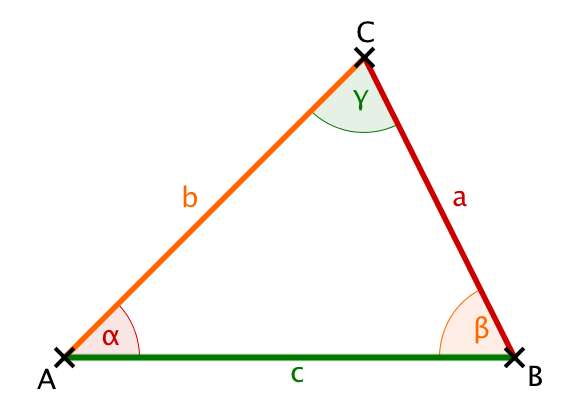
Alternative formulation of the sine theorem
By transformations, the sine theorem can also be brought to the following forms:
The Pythagorean theorem as a special case of the cosine theorem
For we obtain a right triangle with . So the Phthagorean theorem is a special case of the cosine theorem.
Example
Consider a triangle with given values , , and hence also .
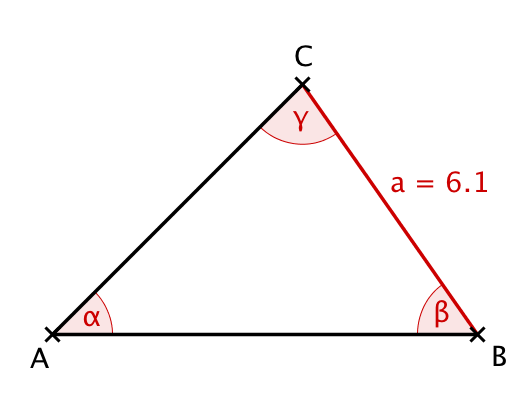
First calculate the length of side using the sine theorem:
Plug in the known values.
Solve for .
Now calculate the length of the side using the cosine theorem:
Plug in the values.