Starting from the normal parabola, one can construct any parabola.
Starting from the normal parabola, one can construct any parabola. For this, you can use the vertex form:
from which you can read off the vertex .
The individual parameters of the vertex form have the following influence on the graph of the parabola:
Parameter | Influence on | Graph |
|---|---|---|
a | Opening direction and extension/compression
| 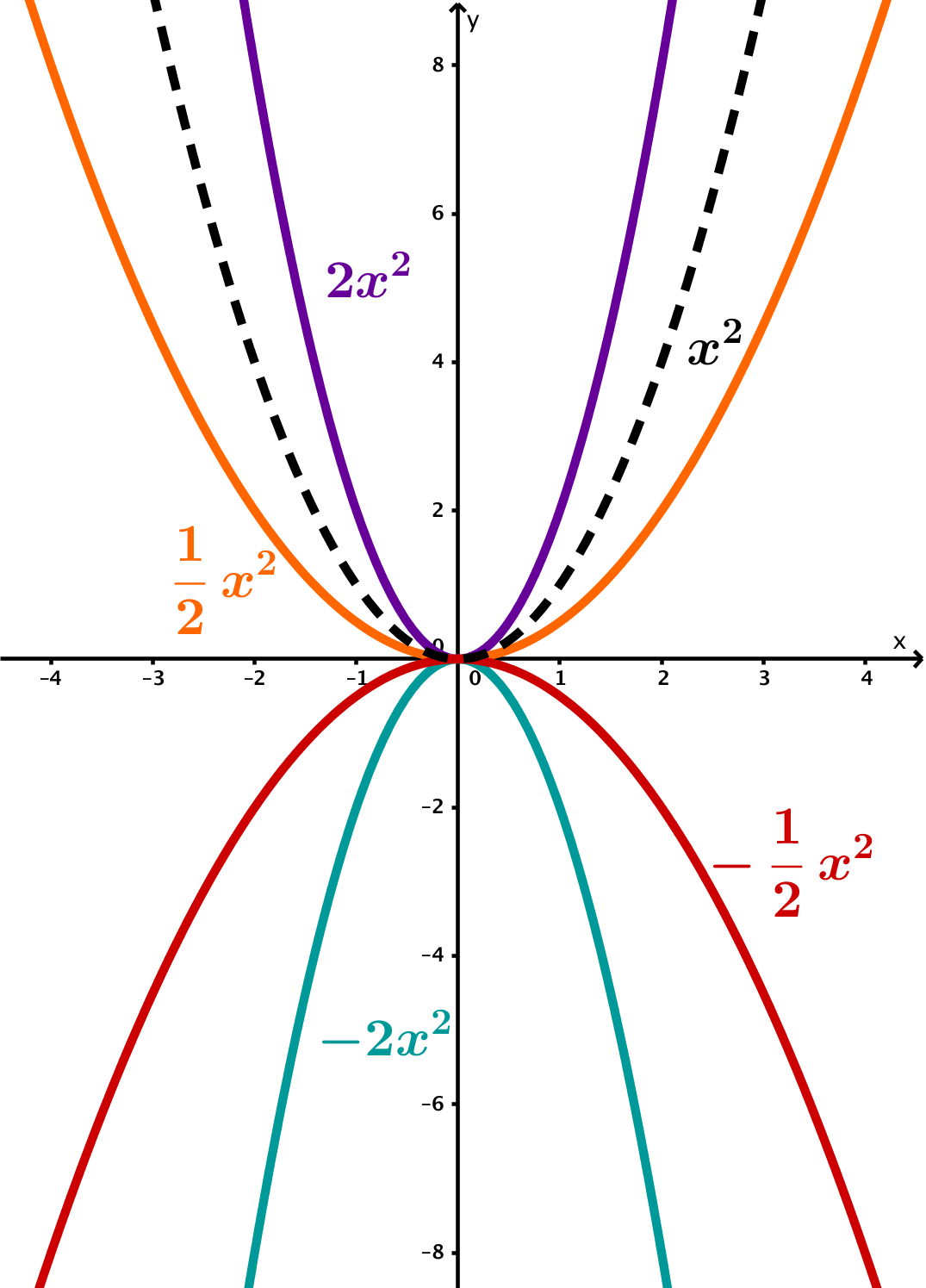 |
d | Shift in -direction
| 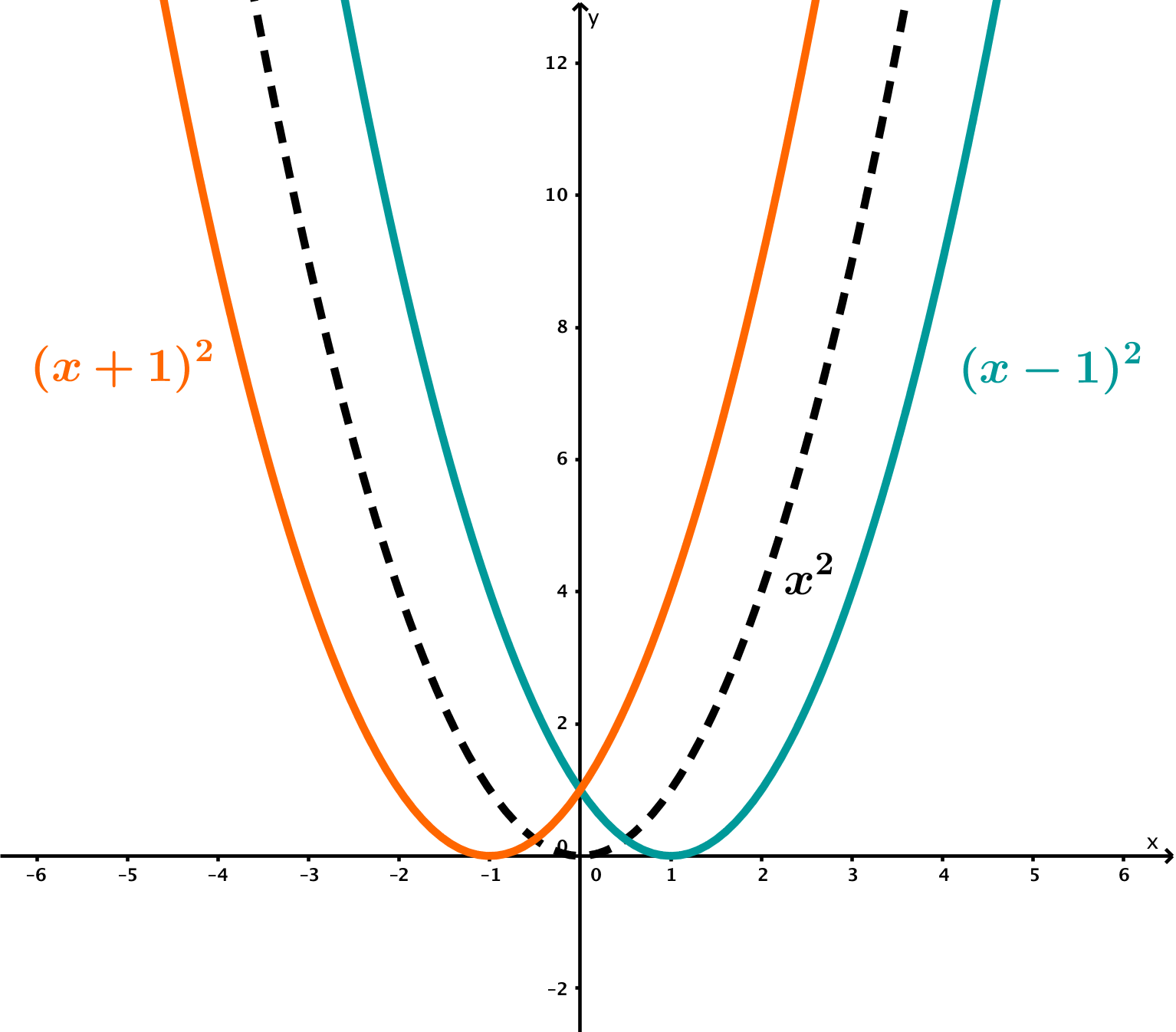 |
e | Shift in -direction
| 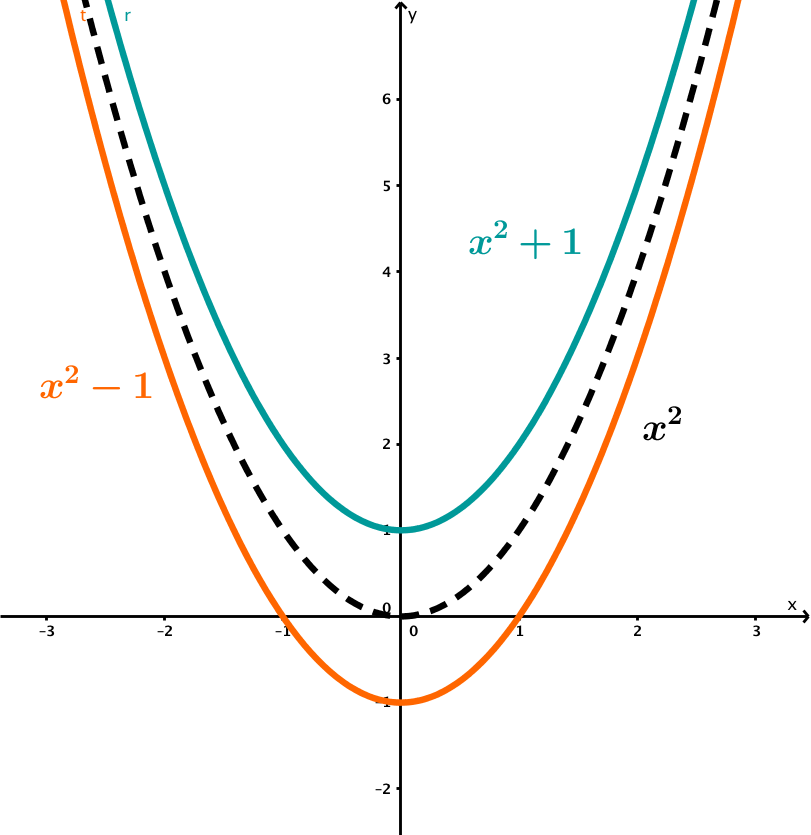 |
Example
Finde zu der nebenstehenden Parabel in dem Koordinatensystem die zugehörige Funktionsgleichung, das heißt mit passenden Parametern . Betrachte in der obigen Tabelle nochmal, welche Auswirkungen die Parameter haben.
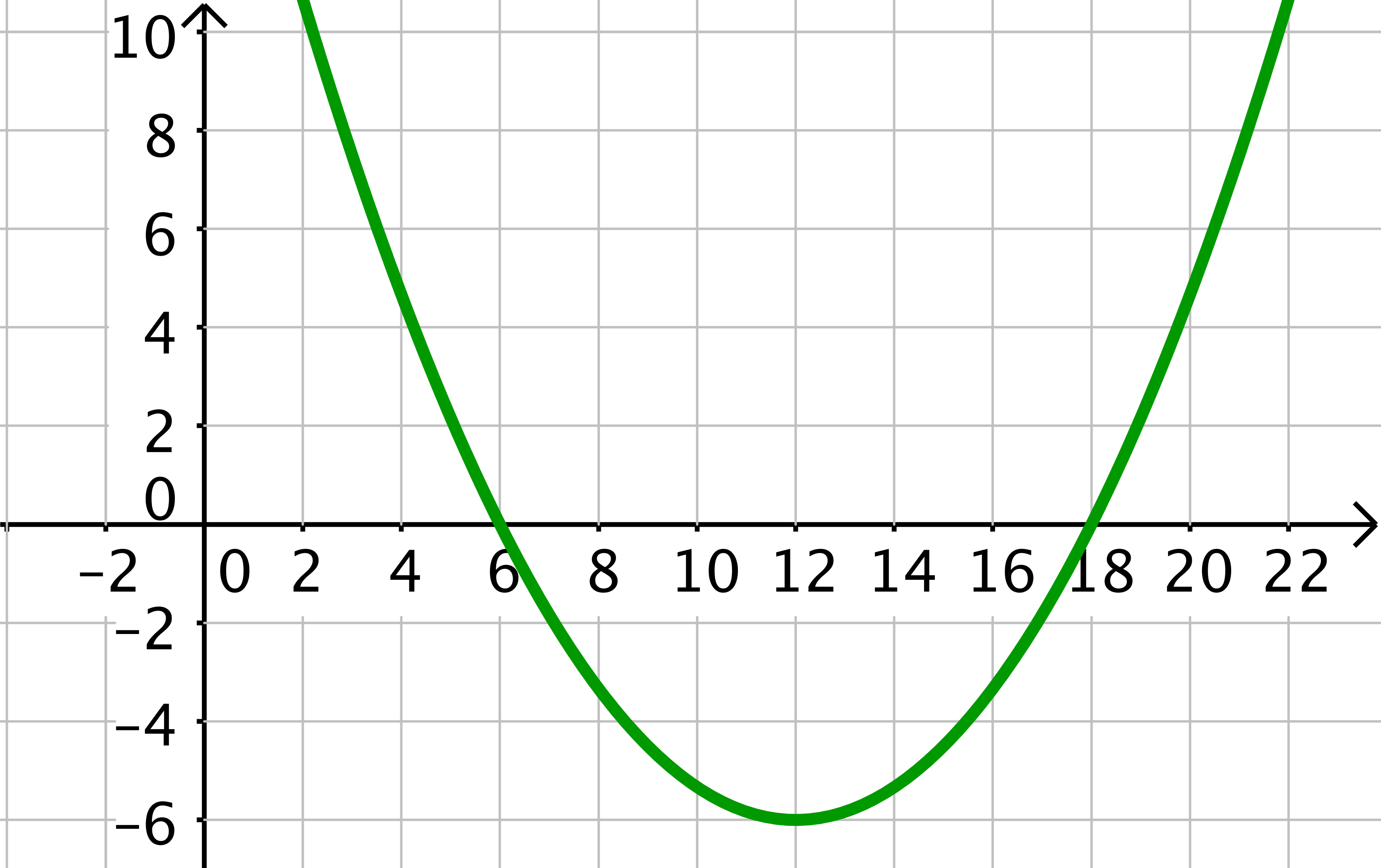
You can recognise the vertex of the parabola in the graph.
Now, the vertex is contained in the vertex form .
The parameter remains to be determined. To do this, you can read off a point from the graph and insert it into the equation of the function. is a point on the graph of
Solve this equation for .
Substitute into the equation of the function.
Visualisation in an applet
Use the sliders to change the parameters.
